Cards terminology
×![]()
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Merchant | A merchant refers to a business or an individual that sells goods or services and accepts payments via payment cards. |
| MCC | A Merchant Category Code (MCC) is a 4-digit number that classifies the type of goods or services a merchant offers. Examples: 4816 - Computer Network/Information Services 5139 - Commercial Footware |
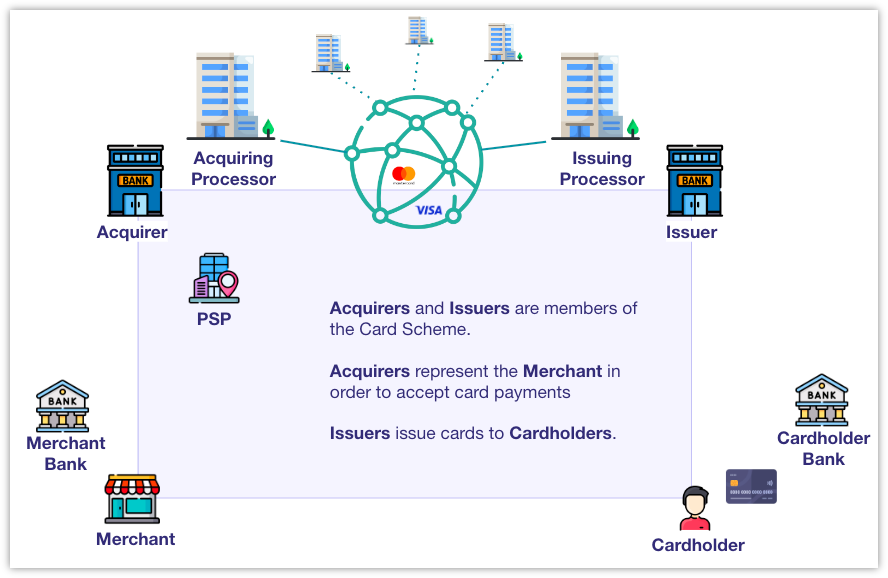
| Card Acquirer | A card acquirer refers to a financial institution or payment service provider that enables merchants to accept card payments from customers. The acquirer establishes and maintains merchant accounts, processes transactions and ensures the funds from these transactions are deposited into the merchant's payment account. |
| Acquiring Processor | An acquiring processor is a third-party company that handles the technical and operational aspects of payment card acquiring on behalf of a card acquirer. Example: Silverflow |
| Card Issuer | See the description here. |
| Payment Card | A payment card refers to a payment instrument issued by financial institutions to their customers, enabling them (the cardholders) to access the funds in their payment account. |
| Issuing Processor | An issuing processor is a third-party company that handles the technical and operational aspects of payment card issuance on behalf of a card issuer. Examples: Marqeta, Worldline. |
| Cardholder | A cardholder refers to an individual or an entity that owns and uses a payment card to purchase goods or services from a merchant. |
| Card Transaction | A card transaction refers to a transaction made by the use of a payment card. For more details see the description here. For card-present transactions (CP), both the cardholder and payment card are physically present, enabling the business to validate the transaction in real time. The cardholder swipes, inserts, or taps the card at a physical POS terminal. Card-not-present transactions (CNP) take place online, where the cardholder cannot present the physical card to the business at the time of the payment. The payment information is provided electronically or verbally. Example: entering card details on an e-commerce website. |
| Card Network | The term card network refers to the physical and operational infrastructure that facilitates the electronic transfer of funds between different parties. The term card network is often used interchangeably with the term card scheme (that focuses on the rules, procedures, and standards), despite the fact that there are subtle differences depending on the context. Examples: Mastercard, Visa, American Express. |
| Card Funding Type | A card funding type defines the way the card is funded. Common funding types include:
|
| Card Category | A card category refers to a classification of payment cards based on the target market:
|
| PAN | A Primary Account Number (PAN) refers to a 12 to 19-digit number that serves as a unique identifier of a payment card. |
| BIN | The Bank Identification Number (BIN) refers to the first 6 or 8 digits of the Primary Account Number (PAN). It identifies the card issuer. |
| Masked PAN | A Masked Primary Account Number (PAN) is a concealed segment of a PAN when displayed or printed, to protect it from anyone who does not have a legitimate reason to see it. Example: 492500******1234 |
| CVV/CVC | The Card Verification Value (CVV) or Card Verification Code (CVC) is a 3 or 4-digit number, usually located on the signature panel on the back of the payment card. It is used as a security measure for card-not-present transactions, where a Personal Identification Number (PIN) cannot be manually entered by the cardholder. Examples: CVV is used by Visa, CVC by Mastercard. |
| PIN | A Personal Identification Number (PIN) is a secret 4 to 6-digit numeric code belonging to the card and serving as a security code. |
| 3DS | Three-Domain Secure (3DS) is a multi-factor authentication protocol that helps to confirm a payer's identity during a card transaction. It acts as an additional layer of fraud prevention in order to comply with Strong Customer Authentication (SCA). |
| Chargeback | See the description here. |